Various TYPES OF THERMO PLASTICS
( CELLULOSE DERIVATIVES & SYNTHETIC RESINS)
Thermo plastics
These kinds of plastics have long separate and large molecules arranged side by side. The various types of thermoplastics are discussed below.
Cellulose derivatives
It is obtained by treating the cellulose with acetic acid. It was first prepared in 1865. It is inserted and compressed in the mould for better stability and for obtaining high mechanical strength. It has the tendency to absorb moisture and is less in weight. It is used for manufacturing photographic films, buttons, radio panels, sheets, tubes, toys etc.,
(ii) Ethyl cellulose:
It is the most lightest of all cellulose derivatives. It has very good electrical properties, chemical resistance, surface hardness and strength. Generally used for making jigs, fixtures, nozzles and moulded articles.
(iii) Cellulose acetate – butyrate:
It is obtained by treating cellulose with acetic acid and butoric acid. It has a good stability against light and heat and moisture absorption tendency. Cellulose acetate can also be used for injection moulding. It is used for making radio cabinets, pipes, steering wheels, handles and coating.
(iv) Cellophane:
It is generally available in extruded form. Cellophane is a thin, transparent sheet made of regenerated cellulose. It has an attractive appearence and good resistance to moisture, solvents and fire. Generally used for making curtains and packing materials.
(v) Cellulose propionate:
It has low tendency for moisture absorption. Cellulose propionate can withstand temperatures up to and can be easily moulded. Used for making fountain pens, telephones and flashlight cases.
Synthetic resins
The following are the synthetic resins.
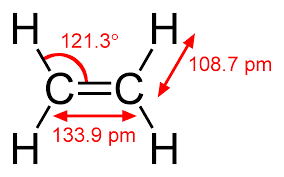
(i) Polyethylenes or polythene (C2H4)n
Polyethylene (abbreviated PE) or polyethene is the most common plastic. These are commercially prepared in America in 1940's. Many kinds of polyethylene are known, with most having the chemical formula (C2H4)n. polyethylene are obtainable as various liquids, gums and tough flexible solids suitable for moulding.
 It has very high resistance to acids, alkalises and the solvents can also be made flexible, tough and good insulators. It has low water absorption. They are wax like in appearance, translucent, odorless and one of the lightest plastics. these are low in cost. These are flexible over a wide range of temperatures.
It has very high resistance to acids, alkalises and the solvents can also be made flexible, tough and good insulators. It has low water absorption. They are wax like in appearance, translucent, odorless and one of the lightest plastics. these are low in cost. These are flexible over a wide range of temperatures.
Uses:
- Polythene film is one of the most lightweight and durable packaging mediums available.
- Plastic packaging makes an important contribution to reducing food spoilage rates by moisture proofing.
- Polythene ducting is compatible with most fans, heaters, air conditioners, air handling units etc.,
- Pipes and tanks for water storage.
- As insulation in submarine cables and radar lines.
- Lining for lagoons to avoid seepage of polluted water into the underground.
- It is used for making fabrics, trays, for corrosion resistant coatings.
Disadvantages:
- Polythene is not biodegradable, and if dumped in the soil causes harm to the plant life, as the toxic substances of polythene get blocked among the soil particles.
- Polythene threatens the life in the water bodies. The chemicals in polythene affects the survival of flora and fauna of the aquatic and marine Eco-systems.
- Polythene is also likely to clog the drains causing problems in the water flow of the pipes. The pipe blockages would cause flooding and the free flow of water is disturbed.
- Polythene is harmful for animals if swallowed. It solidifies inside the abdominal cavity which ultimately becomes lethal to the animal.
- In most households poly bags are used to preserve food items. It has been found out, the colorful poly bags contains lead and cadmium which are toxic and cause adverse effects to human health.
- If polythene is burnt in open air hydrogen cyanide which is carcinogenic (cancer causing) is released.
- Hydrogen cyanide causes environmental pollution and health hazards.
Two types of polyethylene are manufactured depending upon the condition of polymerisation.
(a) High density polyethylene (HDPE)
(b) Low density polyethylene (LDPE)
HDPE | High Density Polyethyelene (HDPE)
A linear polymer, High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is prepared from ethylene by a catalytic process. The absence of branching results in a more closely packed structure with a higher density and somewhat higher chemical resistance than LDPE. High density polyethylene is also somewhat harder and more opaque and it can withstand rather higher temperatures (120° Celsius for short periods, 110° Celsius continuously). High density polyethylene lends itself particularly well to blow moulding. It has specific gravity 0.96.
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE)
LDPE is created by free-radical polymerization. This is obtained by high pressure process. LDPE is defined by a density range of 0.910-0.940 g/cm3, softening temperature 86°c. LDPE has a high degree of short and long chain branching, which means that the chains do not pack into the crystal structure as well. It has, therefore, less strong inter molecular forces as the instantaneous dipole induced dipole attraction is less. This results in a lower tensile strength and increased ductility.
(ii) Polystyrene (PS):
Chemical formula of Polystyrene (PS) is
A high strength plastic is obtained by addition polymerisation in presence of SnCl4 catalyst. It can be toughened by mixing another polymeric material acrylonitrile butadiene to give ABS plastics. It is available in any form and any color and physiologically harmless nature make polystyrene suitable for use in contact with food stuffs. It has good dimensional stabilities and strain resistance. Polystyrene's are easily joined by cementing. It has good electrical properties and negligible water absorption.
Uses:
It is used for making boxes, Lenses, Cases, radio parts, food containers, automobile dash blanks, table ware and insulation parts.
(iii) Acrylic resins (polymethyl methacrylate PMMA):
They are the polymer of methyl methacrylate having trade name "prespex". PMMA is manufactured by addition polymerisation of methyl methacrylate in presence of a peroxide catalyst. It has a high transparency tendency. It is made in any color with high dielectric properties, good strength, resistance to moisture and very good light transmitting power. This material can be casted, injection moulded, extruded and can be stretched into sheets.
Uses:
It is used for manufacturing tubes, hospital equipment's, light weight garments, plates, lamination, display cases, sanitary ware, helmets and valves.
(iv) PolyVinylechloride (PVC):
Chemical formula of Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is
It is generally called as PVC. This is the cheapest and most widely used plastic. They are flexible and rigid. It has good electrical and weather resistance. These are resistant to water and available in variety of colors. The vinylchlorides are formed from hydrochloric acid. Limestone and natural gas or coal. The forms of vinylchlorides are almost unlimited. It is manufactured by addition polymerisation of vinylchloride. Polymerisation is carried out in the presence of catalyst. PVC can be manufactured in expanded or cellular form. It is available in two forms namely flexible and rigid.
Properties:
- Termite proof.
- Tough and durable.
- Anti corrosive.
- Light weight.
- Maintenance free.
- Superb quality.
- Have a pleasing appearance.
- Chemical and moisture resistant.
- Available in wide ranges of colors.
Disadvantages:
- Plastic doors are not suitable for entry doors as they are very of light weight.
- They are not weather proof like wooden or metal doors.
- They cannot resist the harsh environment conditions.
Uses:
- Cable jackets.
- Rubber substitute.
- Fabric coating.
- Rain water goods.
- Flooring and ceiling panels.
- Gramphone records.
- Pipes and fittings of water service.
(v) Polytetra fluoroethylene (PTFE):
It is named after Teflon. The mer of PTFE is represented as CF2 = CF2. PTFE is manufactured by addition polymerisation techniques. Polymerisation is carried out under organic peroxide or oxygen as catalyst.
It has good chemical resistance and can withstand temperatures up to 288°C. It is non-flammable. It cannot be dissolved in any solvent. It has high electrical resistance, low friction and very low adhesion to other substances. It mostly available in the form of sheets, rods and tubes.
Uses:
It is used for making non-stick coating, bearing bushes, piston rings, mouldings in aircraft's, gaskets, electrical insulators, laboratory equipment etc.,
(vi) Nylon (polyamides):
It is also known as polyamide. It is produced by series of condensation reaction between an amine and organic acids. Nylon is produced from the condensation polymerisation reaction between hexamethylene diamine and adipic acid.
It has high strength, toughness and elasticity. It can be moulded and extruded into rods. The powder metallurgy methods can also be used for this type of plastics. It is a good insulator and has good wear resistance. They are resistant to most of the solvents and chemicals.
Uses:
Used for making Yarn for making clothes, insulation wires, moulding gears, bearings and combs.
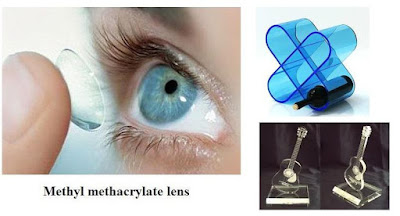
(vii) Poly Methyl methacrylate (PMMA)(Acrylics):
Chemical formula of Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is
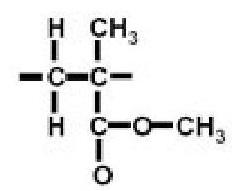 It's trade name is Lucite and Plexiglass. It is easily formed at temperatures around . It is known for its clear color and high light transmission ability.
It's trade name is Lucite and Plexiglass. It is easily formed at temperatures around . It is known for its clear color and high light transmission ability.
Uses:
Used for manufacturing aircraft parts, bowls, contact lenses and various surgical instruments.











No comments:
Post a Comment